Which Terms Refer To Versions Of Dsl Service?
The biggest rival to the cable modem in the broadband Internet business is the digital subscriber line (DSL). DSL, like its predecessor ISDN, appeals to the telephone companies who might be able to use the existing POTS wiring to provide high-speed Internet access. Not every blazon of DSL is suitable for existing wiring; however, all just the fastest, nearly expensive types tin can sometimes be used with the existing POTS institute. DSL is also highly-seasoned to businesses that don't accept access to cable modems but are looking for a high-performance, lower-toll alternative to the expensive ISDN services that acme out at 128Kbps.
Note
Some technical discussions of DSL refer to xDSL. The x stands for the various versions of DSL being proposed and offered by local telephone companies and ISPs. DSL generally is used to refer to whatsoever type of digital subscriber line service.
Ane advantage of DSL compared to its most popular rivalcable modemsis that cable modems share mutual bandwidth, which means that a lot of simultaneous apply by your neighbors can slow down your connection. If y'all utilise DSL you don't take this concern; whatever bandwidth speed y'all pay for is yoursperiod.
How DSL Works
DSL takes advantage of the broadband nature of the telephone system, using the arrangement'south adequacy to behave signals at multiple frequencies to allow both loftier-speed Net traffic and phone calls at the same time. Two methods for sending and receiving signals are used by the most common type of DSL, Asymmetric DSL (ADSL):
-
Carrierless Amplitude/Phase (CAP)
-
Discrete Multitone (DMT)
Nearly early on DSL installations used CAP, which splits the telephone line into three frequency bands. Verbal frequency usage varies by arrangement, but nearly typically, the divisions resemble the post-obit:
-
Voice calls use frequencies from 30Hz to 4KHz. This frequency is besides used by answering machines, fax machines, and alarm systems.
-
Upstream information such every bit web folio requests and sent email uses frequencies betwixt 25Hz and 160Hz.
-
Downstream data such as received spider web pages and email uses frequencies between 240KHz and 1.5MHz.
Some systems use the 300Hz700Hz range for downstream data and frequencies of 1MHz and to a higher place for upstream information.
Because voice, downstream, and upstream data use different frequencies, you lot can talk, surf, and send email at the aforementioned time.
DMT, the system used by most recent ADSL installations, divides the telephone line into 247 channels that are 4KHz wide. If a particular channel has bug, a different channel with meliorate betoken quality is used automatically. Unlike CAP, DMT uses some channels starting at around 8KHz to ship and receive information.
Both types of signaling can have issues with interference from telephones and similar devices, so devices called low-pass filters are used to prevent phone signals from interfering with signals above the 4KHz range, where DSL signals begin. The location of these filters depends on the blazon of DSL you use and whether you are installing DSL service yourself.
At the central switch, DSL data is transferred to a device called a DSL admission multiplexer (DSLAM), which transfers outgoing signals to the Cyberspace and sends incoming signals to the correct DSL transceiver (the correct proper noun for the so-called "DSL modem" that connects to your computer).
Who Tin Use DSLand Who Can't
DSL services accept been slowly rolling out beyond the country for years, commencement to major cities and and so to smaller cities and towns. As with 56Kbps modems, rural and pocket-sized-town users are often the concluding to receive this service. If you live in an area without access to cable or Cyberspace, yous should consider satellite-based or stock-still wireless Net services where available for a faster-than-56Kbps experience.
Just as altitude to a telephone company's primal switch (CS) is an of import consideration for people purchasing an ISDN connection, distance too affects who tin employ DSL in the markets offer it. For example, about DSL service types require that you be within about 18,000 anxiety (near iii miles) wire distance to a telco offering DSL; some won't offer it if you're beyond xv,000 feet wire altitude considering the speed drops significantly at longer distances. Repeaters or a local loop that has been extended by the telco with fiber-optic line might provide longer distances. The speed of your DSL connectedness varies with distance: The closer you are to the telco, the faster your DSL access is. Many telcos that offer some type of DSL service provide websites that help you lot determine whether, and what type of, DSL is available to yous.
If y'all desire to locate DSL service providers in your area, compare rates, and see reviews from users of the hundreds of ISPs now providing DSL service, fix your browser to http://www.dslreports.com. The site provides a verdict on many of the ISPs reviewed, summarizing users' experiences and ranking each ISP in five categories.
Note
If you want to connect DSL to your SOHO or office LAN, check first to run into what the provider's attitude is. Some users report practiced cooperation, whereas others signal they were told "we can't aid yous" or were told that DSL "couldn't be continued to a LAN." Fortunately, as abode LANs continue to proliferate, this is becoming a less frequent problem. Once again, check around for the best policies. Low-cost switch/router combinations from companies such equally Linksys and D-Link and Microsoft'southward Internet Connection Sharing provide relatively piece of cake means to share both DSL and other types of high-speed connections.
Even if your telco's primal switch is well inside wire distance range of your location, that's no guarantee that you qualify for DSL service. The design and condition of the wiring plant connecting your location with the central switch can foreclose you from qualifying for DSL service. Because DSL service depends on successful sending and receiving of loftier-frequency information, a telephone wiring plant that blocks high-frequency signals tin can't be used for DSL service. Some of the typical issues with telephone lines that aren't DSL-friendly include
-
Loading coils. These amplifiers boost voice signals and are sometimes called vocalisation coils. Unfortunately, these block the loftier-frequency signals needed by DSL service.
-
Span taps. Used to extend service to new customers without running separate lines all the style dorsum to the cardinal switch. Bridge taps tin create a circuit that'south too long for DSL service.
-
Cobweb-optic cables. Used to comport a lot of signals in a small physical infinite, fiber-optic cables use analog-to-digital (A/D) and digital-to-analog (D/A) converters where they connect to copper telephone lines. A/D and D/A converters can't laissez passer DSL signals through to their destinations.
Major Types of DSL
Although the term DSL is used in advertisement and popular discussions to refer to whatsoever form of DSL, many, many variations of DSL are used in different markets and for different situations. This section discusses the most common forms of DSL and provides a table that compares the various types of DSL service. Although many types of DSL service exist, you lot can choose only from the service types offered by your DSL provider:
-
ADSL (Asymmetrical DSL). The type of DSL used most often, particularly in residential installations. Asymmetrical ways that downstream (download) speeds are much faster than upstream (upload) speeds. For most users, this is no problem because downloads of web pages, graphics, and files are the major use of Internet connections. Maximum downstream speeds are upwards to 9Mbps, with upwards to 640Kbps upstream. Most vendors who offer ADSL provide varying levels of service at lower speeds and prices, as well. Vox calls are routed over the same wire using a small amount of bandwidth, making a unmarried-line service that carries vocalism and data possible. ADSL is more expensive to prepare up than some other forms of DSL because a splitter must be installed at the client site, significant that you lot must pay for a service call (also called a truck roll) as part of the initial setup accuse.
-
CDSL (Consumer DSL). A slower (1Mbps downstream) grade of DSL that was adult by modem chipset maker Rockwell. It doesn't crave a service call because no splitter is required at the customer site.
-
G.Low-cal (Universal DSL, and also called DSL Light or Splitterless DSL). Another version that splits the line at the telco end rather than at the consumer end. Downstream speeds range from one.544Mbps to 6.0Mbps, and upstream speeds can be from 128Kbps to 384Kbps. This is becoming one of the about popular forms of DSL because it enables consumers to use self-install kits. Note that the DSL vendor might cap the service at rates lower than those listed before in the affiliate; bank check with the vendor for details.
-
SDSL (Symmetrical DSL). This type of DSL service provides the aforementioned speed for upstream as for downstream service. Generally, SDSL is offered to business rather than residential customers because it requires new cabling (rather than reusing existing phone lines). A long-term contract frequently is required.
Tabular array 17.two summarizes the diverse types of DSL.
| DSL Type | Description | Data Rate Downstream; Upstream | Distance Limit | Awarding |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IDSL | ISDN Digital Subscriber Line | 128Kbps | 18,000 feet on 24-gauge wire | Similar to the ISDN BRI service but data only (no voice on the same line) |
| CDSL | Consumer DSL from Rockwell | 1Mbps downstream; less upstream | eighteen,000 anxiety on 24-guess wire | Splitterless home and small business concern service; like to DSL Low-cal |
| DSL Lite (aforementioned every bit Yard.Calorie-free) | Splitterless DSL | From 1.544Mbps to 6Mbps downstream, depending on the subscribed service | eighteen,000 anxiety on 24-gauge wire | Sacrifices speed for not having to install splitters |
| HDSL | High bit-rate Digital Subscriber Line | one.544Mbps duplex on two twisted-pair lines; two.048Mbps duplex on three twisted-pair lines | 12,000 feet on 24-gauge wire | T-1/E1 service between server and phone company or within a company |
| SDSL | Symmetric DSL | one.544Mbps duplex (U.Due south. and Canada); ii.048Mbps (Europe) on a single-duplex line downstream and upstream | 12,000 feet on 24-judge wire | Same as for HDSL merely requiring only one line of twisted pair |
| ADSL | Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line | 1.544Mbps to 8.448Mbps downstream; 16Kbps to 640Kbps upstream | ane.544Mbps at xviii,000 anxiety; 2.048Mbps at 16,000 anxiety; 6.312Mbps at 12,000 feet; eight.448Mbps at nine,000 feet | The virtually common DSL used for Internet access |
| VDSL | Very High Subscriber Line Digital | 12.9Mbps to 52.8Mbps downstream; 1.6Mbps to two.3Mbps upstream | 4,500 feet at 12.96Mbps; three,000 feet at 25.82Mbps; i,000 anxiety at 51.84Mbps | ATM networks; Fiber to the Neighborhood |
With any blazon of DSL, an external device called a DSL modem is attached to the computer through either of the following:
-
A crossover cablevision running to an Ethernet card or port in the reckoner
-
A USB cable running to a USB port in the estimator
An RJ-11 (standard telephone) cable is fastened between the DSL modem and the RJ-11 port that has been prepare for DSL service.
To foreclose telephone signals from interfering with DSL frequencies, splitters or microfilters must be installed on a DSL line. If y'all choose a technician-installed course of DSL, a device called a splitter is used at your location to prevent interference. Splitter-based DSL allows faster speeds than splitterless DSL installations, but the wait for a technician to bear witness up and add together the splitter tin can add together days or weeks to your installation procedure.
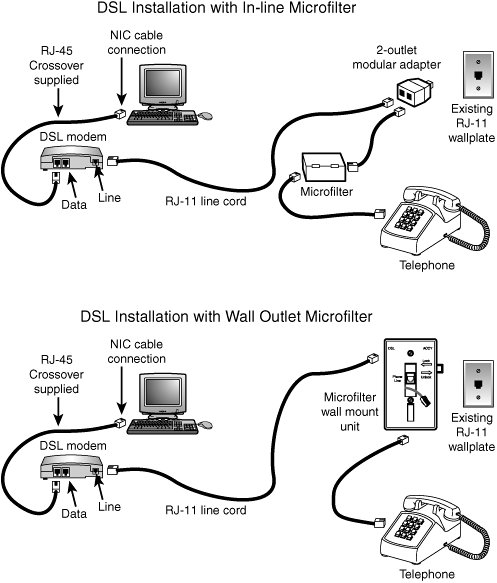
If yous self-install DSL, you will install small devices called microfilters to block interference from telephones, answering machines, and like devices. These devices might fit behind the faceplate of the wall outlet used for DSL service or inline between the phone, answering machine, or fax motorcar and the wall outlet (see Figure 17.ii).
Effigy 17.2. Ii types of DSL self-installations; if a splitter is used to set up a separate DSL line, the microfilters shown here are not necessary.
Tip
If you lot accept a security system attached to your telephone line, scout out for bug if you select DSL as your preferred broadband access method. Security systems are often designed to seize the line, interrupting a phone call in progress to send an alert to the security company. This feature won't work with normal microfilters, then you should purchase a special DSL Warning filter to allow your alarm organisation to coexist with your DSL installation. Get more information nearly the alarm microfilter and culling DSL installation options from www.hometech.com/learn/dsl.html.
DSL Pricing
DSL pricing varies widely, with unlike telephone companies offering different speeds of DSL and unlike rates. Ane thing that's true almost the most unremarkably used flavors of DSL is that they are ordinarily an asymmetrical servicewith download speeds faster than upload speeds. ADSL installations can typically be run over existing copper wires, whereas SDSL installations usually require that new high-quality copper wires exist installed betwixt the CO and the subscriber's location.
For unlimited use, typical residential DSL pricing ranges anywhere from $15 to $eighty a month depending on whether yous want a static or dynamic IP accost and the download speed, which ranges from 256Kbps to 1.5Mbps. Business DSL pricing ranges from $50 to as high equally $500 per calendar month.
The wide variance is partly due to the upload speeds permitted. The lower-cost plans typically use a lower upload speed (some variation on ADSL or M.Low-cal); in contrast, the more expensive plans often utilize SDSL. Cheque carefully with your vendor because your traditional phone company might non be the just DSL game in town. Some major cities might accept as many as half a dozen vendors selling diverse flavors of DSL.
DSL Security Issues
Dissimilar other types of broadband admission, DSL is a straight i-to-one connection that isn't shared; yous take no digital "neighbors" who could casually snoop on your activities. Notwithstanding, as with any broadband "e'er-on" connexion, intrusion from the Internet to your computer is a very real possibility and y'all should safeguard your system behind a router with firewall capabilities. Using an boosted software firewall, such as the i included with Windows XP, is too a practiced thought.
| | For more data on securing whatever type of Internet access, run across "Securing Your Internet Connection," p. 1075. |
Technical Bug with DSL
Telecommunications has always had its share of difficulties, starting with the incredibly irksome and trouble-plagued 300bps modems used on early PCs, only as speed increases, and so practise issues. DSL connections are often very difficult to get working correctly considering DSL, as you've seen, combines the bug of adding high-speed information access to the telephone line with network configuration using TCP/IP (the near powerful and most complex network protocol in widespread utilize; see Chapter xviii, "Local Surface area Networking," for details).
A review of comments from DSL users in various forums, such as DSLReports.com and others, shows that the most common issues include the following:
-
Poor coordination between the DSL sales section of the telco or 3rd-party provider and the installers. This tin can atomic number 82 to cleaved or very late appointments for installation; if possible, contact the installer company to verify the appointment. If possible, opt for a self-install version of DSL to avert bug with belatedly or missing appointments.
-
Installers who install the hardware and software and then exit without verifying it works properly. Enquire whether the installer carries a notebook figurer that tin can test the line; don't permit the installer leave until the line is working.
-
Poor technical back up before and subsequently installation. Record the IP address and other data used during the installation; read reviews and tips from sources listed earlier in the chapter to help yous discover meliorate DSL providers and solutions you can apply yourself or enquire your telco or provider to perform.
-
Lower speeds than anticipated. This can be due to a poor-quality connection to the telco from your dwelling or business or bug at the key switch; inquire the installer to test the line for you during initial installation and tell you the top DSL speed the line tin can accomplish. On a salubrious line, the problem is often traceable to a very low value for the Windows Registry central called RWIN (receive window), which should be adjusted from its default of 8192 (8KB) to a value equally high as 32768 (32KB) or even 65535 (64KB). If your system previously was used with a dialup modem, the value for RWIN can be as low as 2144; low values strength your DSL connection to receive data at rates inappreciably faster than those for a dialup modem connection. For interactive tests that will assist yous notice the best value to use for RWIN or other Registry options, observe line problems, and adjust your configuration, get to http://www.dslreports.com and follow the Tools link from the home page.
Considering of the problems with trying to retrofit an aging vox-oriented telephone network with high-speed Internet service, many pure DSL companies are having financial problems. Some once-prominent DSL ISPs went out of business organization in 20002001, leading to service cancellations in some cases. Earlier you sign a long-term contract for DSL service, you should make up one's mind what your options are if your telco, DSL line provider, or ISP drops DSL service.
Source: https://flylib.com/books/en/4.57.1.169/1/
Posted by: cookgrencir1939.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Terms Refer To Versions Of Dsl Service?"
Post a Comment